Rethinking physics in the era of deep learning is an increasingly important topic. This topic is special because, in addition to data, one can leverage a vast library of physical prior models (e.g. kinematics, fluid flow, etc) to perform more robust inference. The nascent sub-field of physics-based learning (PBL) studies this problem of blending neural networks with physical priors. While previous PBL algorithms have been applied successfully to specific tasks, it is hard to generalize existing PBL methods to a wide range of physics-based problems. Such generalization would require an architecture that can adapt to variations in the correctness of the physics, or in the quality of training data. No such architecture exists. In this paper, we aim to generalize PBL, by making a first attempt to bring neural architecture search (NAS) to the realm of PBL. We introduce a new method known as physics-based neural architecture search (PhysicsNAS) that is a top-performer across a diverse range of quality in the physical model and the dataset.
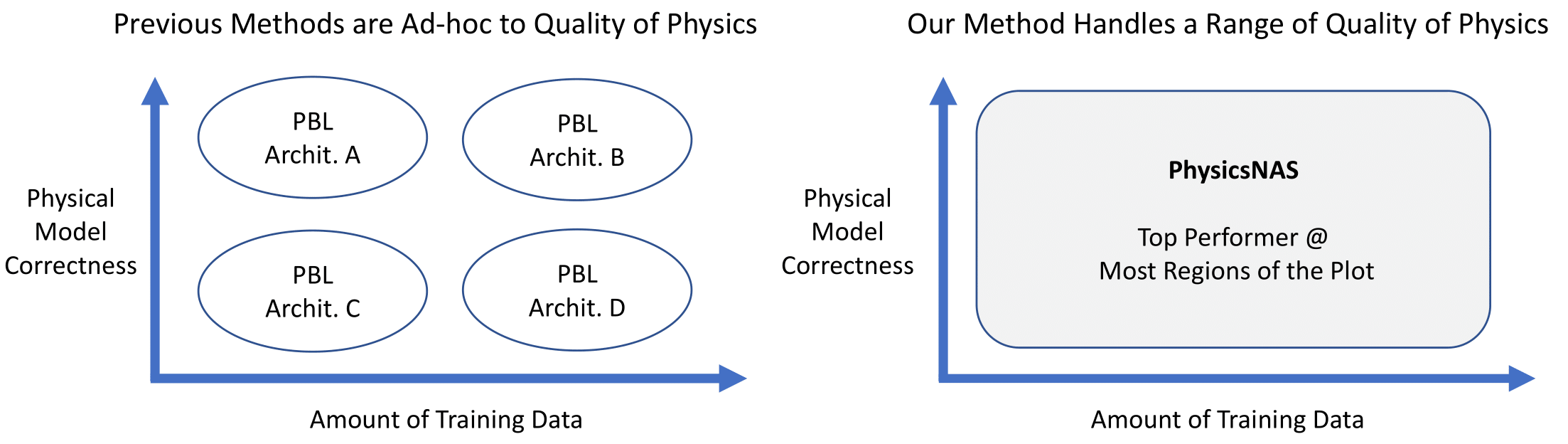
Generalizing PBL across a range of sparsity in training data and correctness in the physical model.
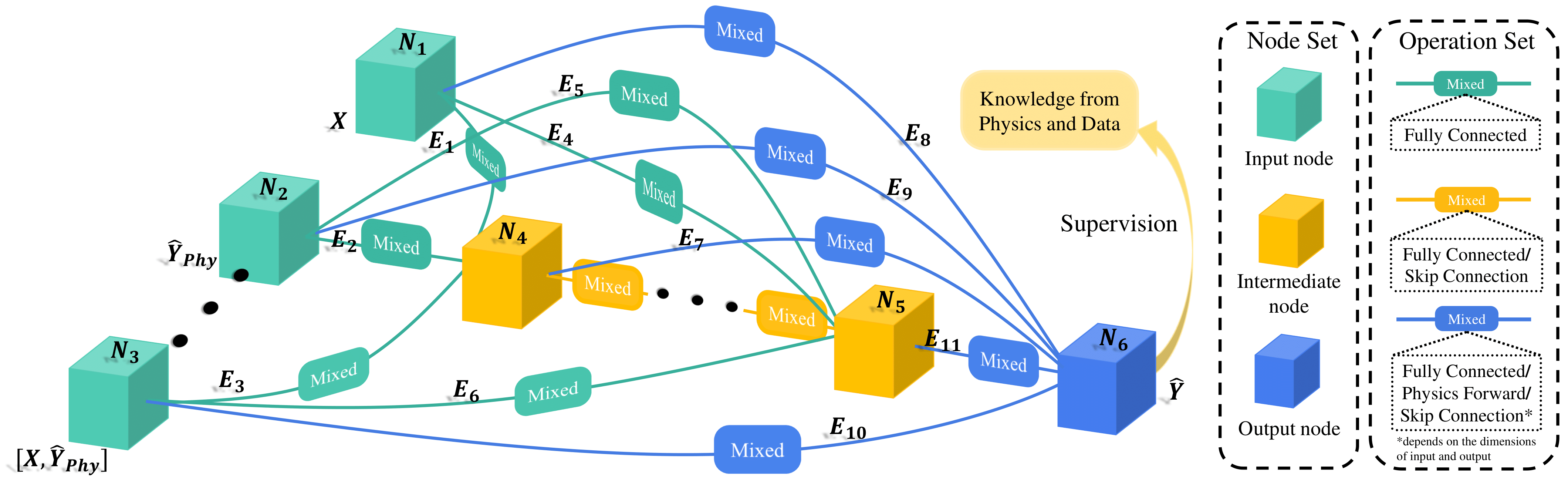
Search space of our PhysicsNAS. In the proposed PhysicsNAS, all the nodes are densely connected by mixed operators from predefined candidate operation sets. The hidden nodes can obtain information from the original inputs or from previous hidden nodes within this search setup. The training process is supervised by both ground truth and physical constraints.
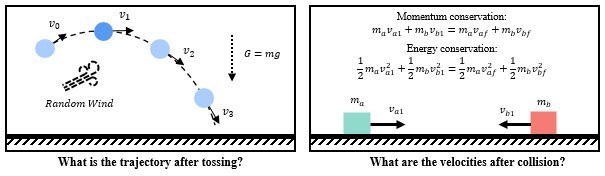
We evaluate our method on a simulator of classical tasks. The first task (Left) is predicting the trajectory of a ball being tossed, and the second task (Right) is estimating the velocities of two objects after collision.
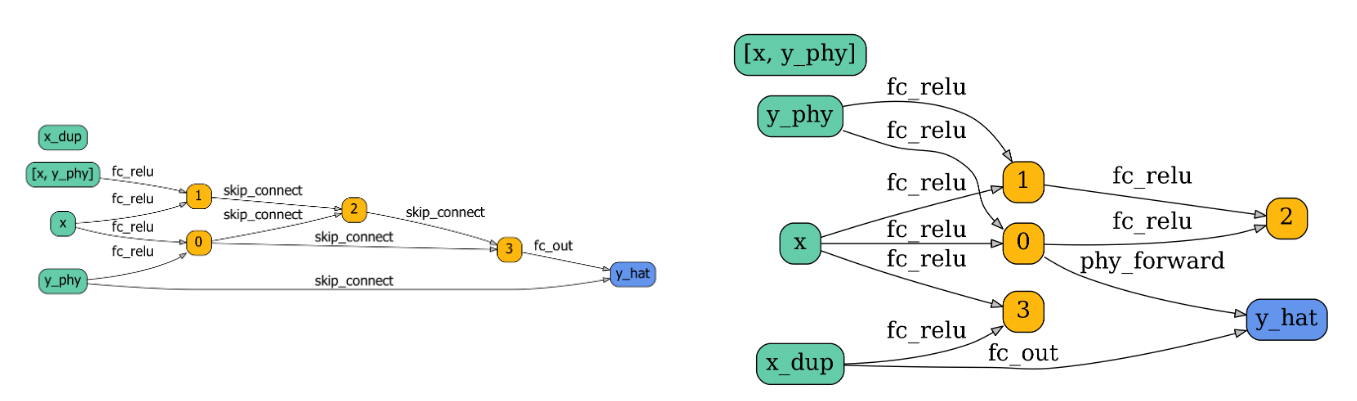
Utilization of physical operations in PhysicsNAS. The selection of physics-inspired operation depends on its accuracy. PhysicsNAS tends to utilize the physical operations when they are more accurate (like the elastic collision model), and prefers a residual connection when they are inaccurate (like the parabola equation).
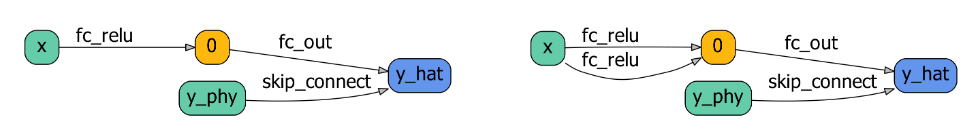
Failure case. In rare situations, a single-stream network could be preferred. PhysicsNAS is unable to converge to single-stream architectures due to the edge selection mechanism.
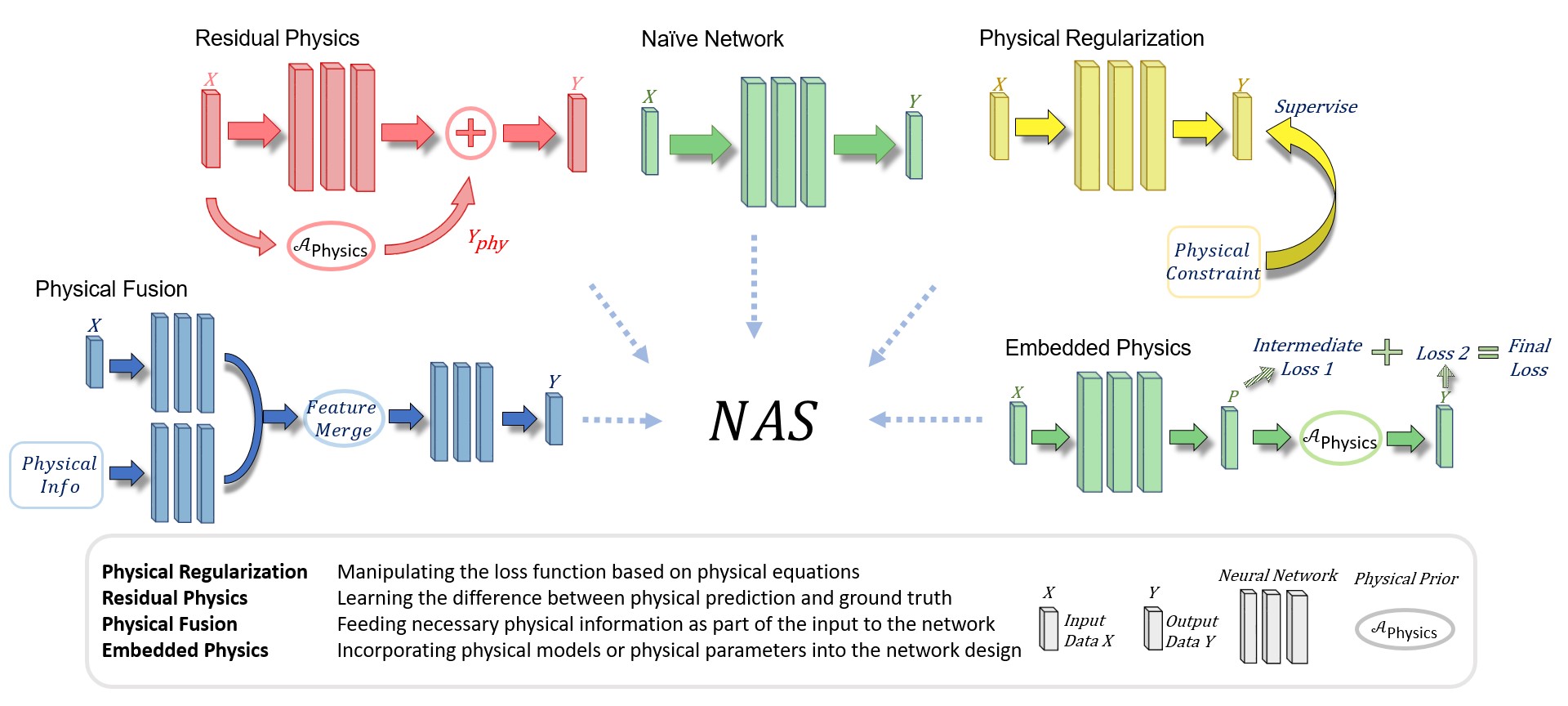 An overview of proposed NAS-based blending approach.
An overview of proposed NAS-based blending approach.




